Hemangioblastoma
Hemangioblastoma
Hemangioblastomas are rare tumors that occur in blood vessels of the brain and spinal cord. They may appear anywhere in the brain but are most often found in the cerebellum and the brainstem in the lower back section of the skull called the posterior cranial fossa. It is estimated that hemangioblastomas make up 8 percent to 12 percent of the tumors in this region but only 1 percent to 2.5 percent of all brain tumors. Sometimes these tumors occur in other sites such as the spinal cord and retina. They may be associated with other diseases such as polycythemia (increased blood cell count), pancreatic cysts and Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome (VHL syndrome).
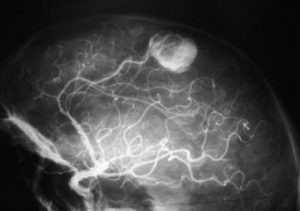
Because these tumors involve blood vessels, they pose a threat of rupturing, and because they tend to grow slowly, they may go undetected for months or years. A previously undiagnosed hemangioblastoma sometimes ruptures – causing bleeding into the brain –before any other symptoms occur.
Symptoms
- Hemangioblastomas typically occur in adults and become symptomatic from age 30 into the 50s.
- Signs and symptoms of hemangioblastoma include headaches, nausea/vomiting, difficulty with balance and dizziness/vertigo.
Diagnosis
- The mass itself is found on either computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. These scans may show signs of acute or previous hemorrhage either into the tumor or around it.
- In addition to the above scans, cerebral angiography is often used to determine the degree of vascularity.
Treatment
- Surgical treatment may correct sporadic hemangioblastoma.
- Radiation therapy (XRT) may be useful to reduce tumor size or to retard growth. However, XRT does not prevent regrowth following surgery.
- Gamma Knife Radiosurgery as well as LINAC have also been employed to successfully treat recurrence and control tumor growth of cerebellar hemangioblastomas
References
http://www.braintumortreatment.com/Latest-News/Hemangioblastoma-.aspx
http://neurosurgery.ucla.edu/hemangioblastomas